Educational Theorists or Educational thinkers are researchers who investigate and explore the different ways in which a human mind learns things. No two minds are the same and every single person has a unique way of learning. Psychologists and educational theorists have researched extensively to understand the different ways how students learn. Educational theory is a pressing priority for all aspiring teachers who intend to teach students one day.
Educational learning theories often involve these two things - one, different kinds of learning and their benefits; two, the role of the teacher in recognizing the various learning ways and imparting knowledge to students by judging their learning parameters. In educational institutions, creating a learner-centered teaching atmosphere is of utmost importance.
Thus, it is essential for teachers who are the practitioners of educational theories to be well-versed in them. There are six important educational theorists that you should read about if you aim to be a practitioner of educational theories someday. Here is your educational theorists' cheat sheet:
- Learning Theories in Education
- Education Theorists List
- FAQs on Educational theorists and their theories chart
Learning Theories in Education
Learning educational theories began in earnest in the 20th century but it can be traced back to Greek philosophers such as Aristotle, Plato, and Socrates. In the 19th century, learning theory’s objective was created from a solely scientific perspective which emphasized first discovering the process by which people learned and then developing teaching methods accordingly.
In the 20th century, debates surrounding educational theories situated behaviourist theory against cognitive psychology. Put in simple words, thinkers started exploring whether people learn by dealing with external factors or by employing their brains in creating knowledge from external information.
There are five major learning theories in education. They are connectivism, behaviorism, constructivism, cognitivism, and humanism. Some more theories may involve transformative, social, and experiential factors too.
- Learning Theory#1: Behaviourism
In this learning theory, studying was to be done in a routined manner wherein knowledge was drilled into the mental bank of students so that they remember them. Teachers also had a big role to play in appreciating the students’ good work and rewarding them.
- Learning Theory#2: Constructivism
This theory proposes that people learn not by passively injecting information but by constructing their own knowledge.
- Learning Theory#3: Cognitivism
In this learning theory, the mind is used as an information processor. It is heavily focused on mental processes - on how the information is taken, sorted, stored, and retrieved.
- Learning Theory#4: Connectivism
As the name suggests, this learning theory believes that learning is done at its best when learners connect with one another by forming social networks. George Siemens introduced this learning theory.
- Learning Theory#5: Humanism
This learning theory believes that a person’s environment and mood have a heavy influence on his learning process. 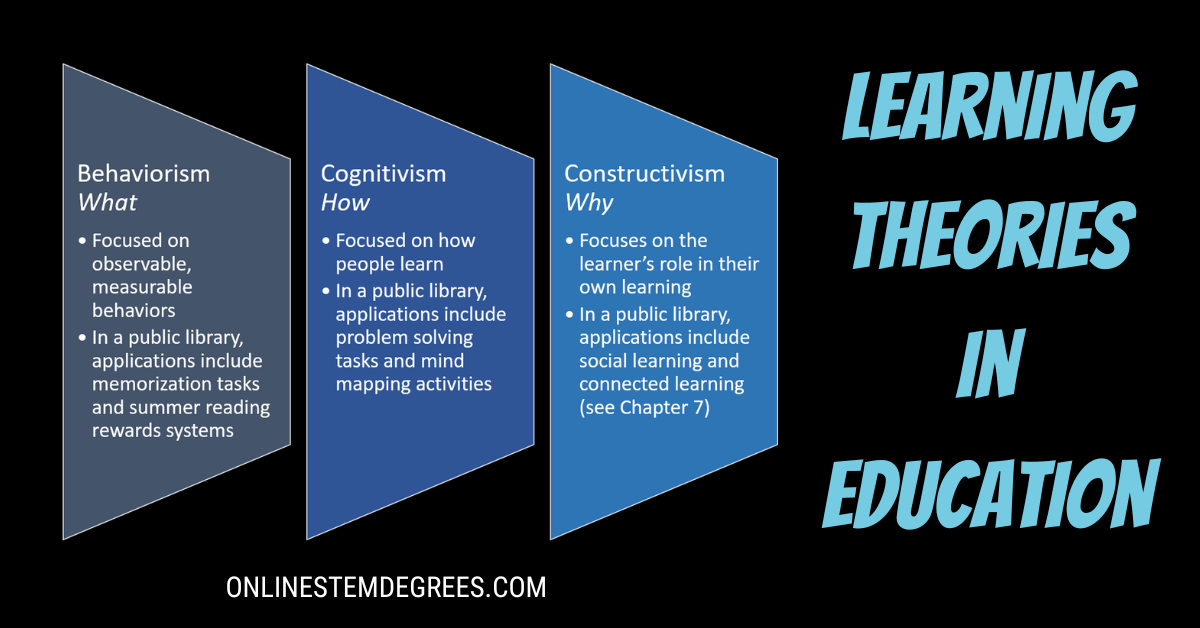 Read ahead to find more about the educational theorists who proposed most of these learning theories.
Read ahead to find more about the educational theorists who proposed most of these learning theories.
Education Theorists List
Following is the list of Six Education Theorists That All Teachers Should Know. So, check out and learn them for betterment:
- Lev Vygotsky
- Jean Piaget
- B.F. Skinner
- Jerome Bruner
- Benjamin Bloom
- Howard Gardner
1. Lev Vygotsky
Famously known for his sociocultural theory, Lev Vygotsky was a Russian psychologist who had a profound influence on children’s learning. He proposed a theory that suggested that children’s learning is heavily influenced by social interaction. They are mostly guided by imitating their surroundings, and by collaborative learning.
Their learning is led by the influences exerted through society and culture. His ‘Zone of Proximal Development theory emphasised the gap produced between what a child independently can learn and achieve, and what the child can learn with encouragement and proper guidance.
For instance: If you assign a child the task of solving a jigsaw puzzle by himself for the first time, it is obvious that he won’t be able to carry it out. But, with proper guidance and help from a guide, there is a chance that he will go all the way and solve it! This will instill in him the necessary skills required to solve jigsaws in the future.
This proved to be one of the best theories of teaching methods too! So, the takeaway from Vygotsky’s theory is the role of the teacher or the parent in guiding the students to complete a task that they cannot complete by themselves. This is called Scaffolding which entails altering the level of guidance to satisfy different learning abilities of children.
2. Jean Piaget
Much like Vygotsky, Jean Piaget was also an educational theorist who focused on child development theories. He was a psychologist too. His theory regarding learning is distinctively different from others. Piaget situated great significance on child education. He investigated the entirety of children’s minds. His child-development theory is still taught in places where students are exposed to pre-service education.
According to Piaget, children develop schemas of knowledge. The term ‘Schemas’ means the building blocks of knowledge. These schemas are a random collection of connected ideas which involve things from the real world. This development grooms them to respond accordingly. After a child develops a schema that enables them to make sense of the world around them, they reach a state of ‘Equilibrium’.
Now, in a child, while responding to a new situation, an assimilation of the schema happens. When the existing schema is no longer useful, then accommodation occurs to introduce new changes. Once the existing schema is accommodated, again a state of equilibrium is achieved. The 4 stages of cognitive development according to Piaget are:
- Sensorimotor stage
- Preoperational stage
- Concrete Operational Stage
- Formal Operational Stage
3. B.F. Skinner
B.F. Skinner, famously known for his work on the behaviorist theory of learning, was one of the major American psychologists in the late 20th century. He was a Harvard professor who explored that in behaviorist theory of learning, learning becomes a way of conditioning within an environment filled with various stimuli and offering ‘reward and punishment’.
According to Skinner, behavior is affected by what has occurred before (the antecedents) and what occurs after (the consequences). This conditions our learning mind. Most classroom education is heavily influenced by his learning theory which in Skinner’s time heavily contributed to ‘progressive’ education reforms. Scaffold believed that modifying the classroom environment will most definitely modify the student’s behavior.
For example, Skinner did not approve of resorting to punishments to right the wrong in a classroom. They are rather counterproductive. He believed in rewards and reinforcements. If the teacher praises or rewards the students for doing the right thing or for displaying good work, this will help operantly condition them to strive for more rewards and hence indulging in doing the right thing appropriate to a classroom. Do Refer: Bilingual education
4. Jerome Bruner
Famously known for his work on human cognitive psychology and his three ‘modes of representation’, Jerome Bruner was an American psychologist. Bruner introduced the idea of a spiral curriculum. Bruner proposed that children can comprehend complex information through a structured way of teaching. Once they are taught the difficult concepts in a simplified form and then made to revise them in their original complex form proves to be a much more fruitful way of teaching.
He advised that the subject be taught in a manner of increasing level of complexity. He also introduced to us the idea of discovery learning. In this learning theory, the learners create their knowledge. So, if students in a classroom discovered knowledge instead of being just told by their teachers, it would be a more effective way of learning.
5. Benjamin Bloom
Bloom was one of the most influential educational theorists of the late 20th century. Bloom was more focused on the role of higher forms of thinking such as analyzing concepts rather than just understanding them. He advocated for mastery over learning through evaluation of concepts rather than just rote learning them. Bloom intended to organize educational goals based on their cognitive complexity. This led him to create Bloom’s Taxonomy.
This hierarchical model focuses on the categorization of educational learning aims and objectives into different levels of specificity and complexity. They are further divided into a tripartite structure as follows - cognitive domain, affective domain, and psychomotor domains. Bloom emphasized that being able to recall the information they have acquired is necessary for them to analyze and apply it for practical purposes. This paves the way for a better learning process.
6. Howard Gardner
The Father of multiple intelligences, Howard Gardner was one of the well-known educational theorists. He explored that people have multiple ways to process information. He also discovered that a typical IQ result does not entirely measure one’s intelligence. Therefore, he created his theory of multiple intelligences which proposed that the mind consisted of “computers” that function almost independently.
And these functioning “computers” lead to several mental abilities. Gardner initially pointed out eight such bits of intelligence that aid our mental abilities but upon researching further, added two others namely - naturalist intelligence, and existential intelligence. Also Read: Why is education important
FAQs on Educational theorists and their theories chart
The six top educational theorists are - Lev Vygotsky, Jean Piaget, and B.F. Skinner, Jerome Bruner, Benjamin Bloom, Howard Gardner. Some among them are educational psychology theorists.
They are Behaviourism, Constructivism, Cognitivism, Brain-based, humanism, and 21st-century skills.
Behaviourism is the first and oldest learning theory that can be traced back to Aristotle and his time.
Concluding Thoughts
We hope that this list of educational theorists helped you grasp the origin of some of the modern-day educational theories practiced in educational institutions. You can read about them in detail to understand the nuances of their theories. To read other education-related articles, check out our page onlinestemdegrees.com. We update articles regularly about education, university rankings, infotainment, and current events.